The Balanced Scorecard provides organizations with a holistic performance measurement system. It aligns strategic objectives, enhances decision-making, and fosters continuous improvement for long-term success.
In the fast-paced and ever-evolving world of business, success hinges on more than just financial metrics. As companies strive for sustainable growth and long-term success, a comprehensive and balanced approach to performance measurement becomes paramount. Explore the Balanced Scorecard – a strategic management framework that has revolutionized the way organizations evaluate and manage their performance.
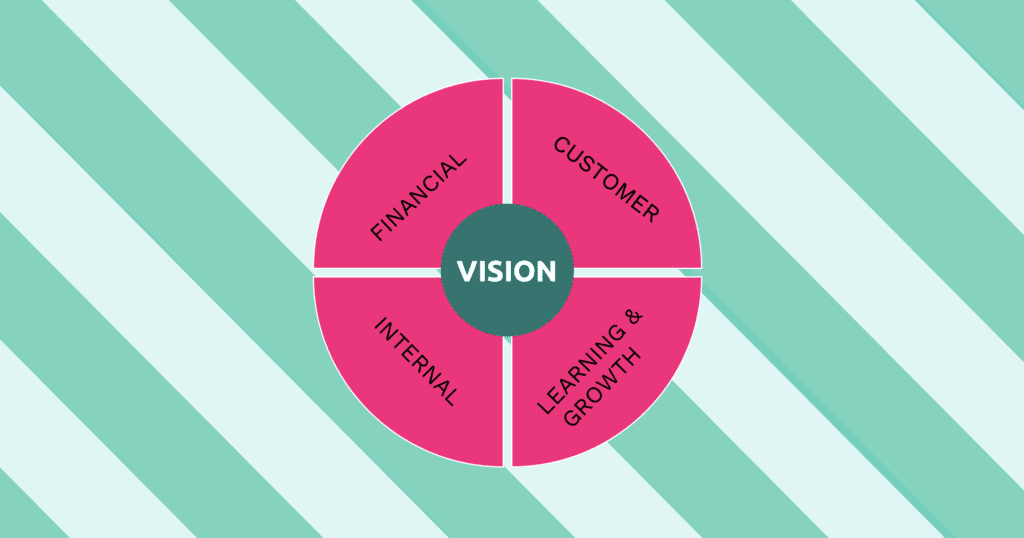
The Framework was developed by Robert Kaplan and David Norton in the early 1990s. The Balanced Scorecard offers a holistic view of an organization’s performance by encompassing four key perspectives. Financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. The concept of the Balanced Scorecard hinges on the understanding that financial measures alone are not sufficient. Indeed, they do not provide a complete picture of a company’s performance and progress toward its strategic objectives.
Four key perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard
The Financial Perspective
This perspective focuses on traditional financial metrics such as revenue growth, profitability, return on investment and cash flow. It provides an understanding of how the organization is performing financially.
Example: XYZ Electronics aims to achieve a 15% increase in annual revenue, maintain a profit margin of at least 20%, and achieve a 10% ROI.
The Customer Perspective
This perspective examines the organization from the customer’s viewpoint, incorporating measures related to customer satisfaction, loyalty, retention, and market share. Consequently, understanding customer needs and preferences is critical for long-term success.
Example: XYZ Electronics targets a customer satisfaction score of 90%, a customer retention rate of 80%, and aims to capture 25% of the market share in its target regions.
The Internal Processes Perspective
This perspective evaluates the internal processes and operations that are essential for delivering value to customers and, subsequently, achieving financial objectives. It includes metrics related to process efficiency, quality, and innovation.
Example: XYZ Electronics aims to reduce product defect rate to less than 1%, decrease manufacturing cycle time by 20%, and improve new product development cycle time by 15%.
Learning and Growth Perspective
This perspective focuses on the organization’s ability to learn, innovate, and develop its people and infrastructure. It includes indicators related to employee training, skill development, knowledge management, and technological capabilities.
Example: XYZ Electronics plans to invest 5% of its budget in R&D, provide 40 hours of training per employee annually, and maintain an employee engagement score of 85%.
Benefits of a Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard offers numerous tangible benefits for organizations seeking to achieve excellence and long-term success. By incorporating the Learning and Growth Perspective, businesses can nurture a culture of continuous learning and innovation. Empowering their employees to develop essential skills and stay updated with the latest technological advancements. Investing in research and development fosters creativity and drives product and service improvements. Maintaining a high employee engagement score is crucial for ensuring a motivated and committed workforce. By embracing the Balanced Scorecard approach, businesses can foster a more balanced and integrated method of performance measurement. This approach aligns strategic objectives with day-to-day operations, promoting a cohesive organizational direction. Moreover, it supports data-driven decision-making, allowing companies to effectively track progress and adjust strategies as needed.
Ultimately, the real benefits of the Balanced Scorecard lie in its ability to enhance organizational performance. Furthermore, this approach optimizes operational processes while also propelling companies toward sustainable growth. It cultivates a competitive advantage in today’s dynamic business landscape, ensuring they remain agile and responsive to market changes.